Implementing FIDO2 Authentication: A Developer's Step-by-Step Guide
Discover the essentials of FIDO2 authentication implementation in this developer-focused guide. We'll walk you through the process step-by-step, covering key concepts, best practices, and code examples to help you integrate secure, passwordless login into your applications efficiently.
- Intro
- Why FIDO2?
- Implementation Overview
- Step-by-Step Guide
- Common Challenges & Solutions
- Testing Your Implementation
- Security Best Practices
Introduction to FIDO2 Authentication
FIDO2 is the latest set of specifications from the FIDO Alliance, aiming to enable passwordless authentication. It comprises two main components:
- WebAuthn API: A web standard published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) that allows web applications to use public-key cryptography instead of passwords.
- Client to Authenticator Protocol (CTAP): A protocol that enables an external authenticator (like a hardware security key) to communicate with the client (like a web browser).
Key Benefits of FIDO2:
- Enhanced Security: Uses asymmetric cryptography, reducing the risk of credential theft.
- Improved User Experience: Eliminates the need for passwords, making authentication seamless.
- Phishing Resistance: Credentials are bound to specific origins, mitigating phishing attacks.
Why FIDO2?
Before diving into the implementation, let's understand why FIDO2 is worth your time:
✅ No More Password Headaches
- Zero password storage
- No reset workflows needed
- Reduced support costs
✅ Superior Security
- Phishing-resistant
- Uses public key cryptography
- Eliminates credential database risks
✅ Better User Experience
- Fast biometric authentication
- No passwords to remember
- Works across devices
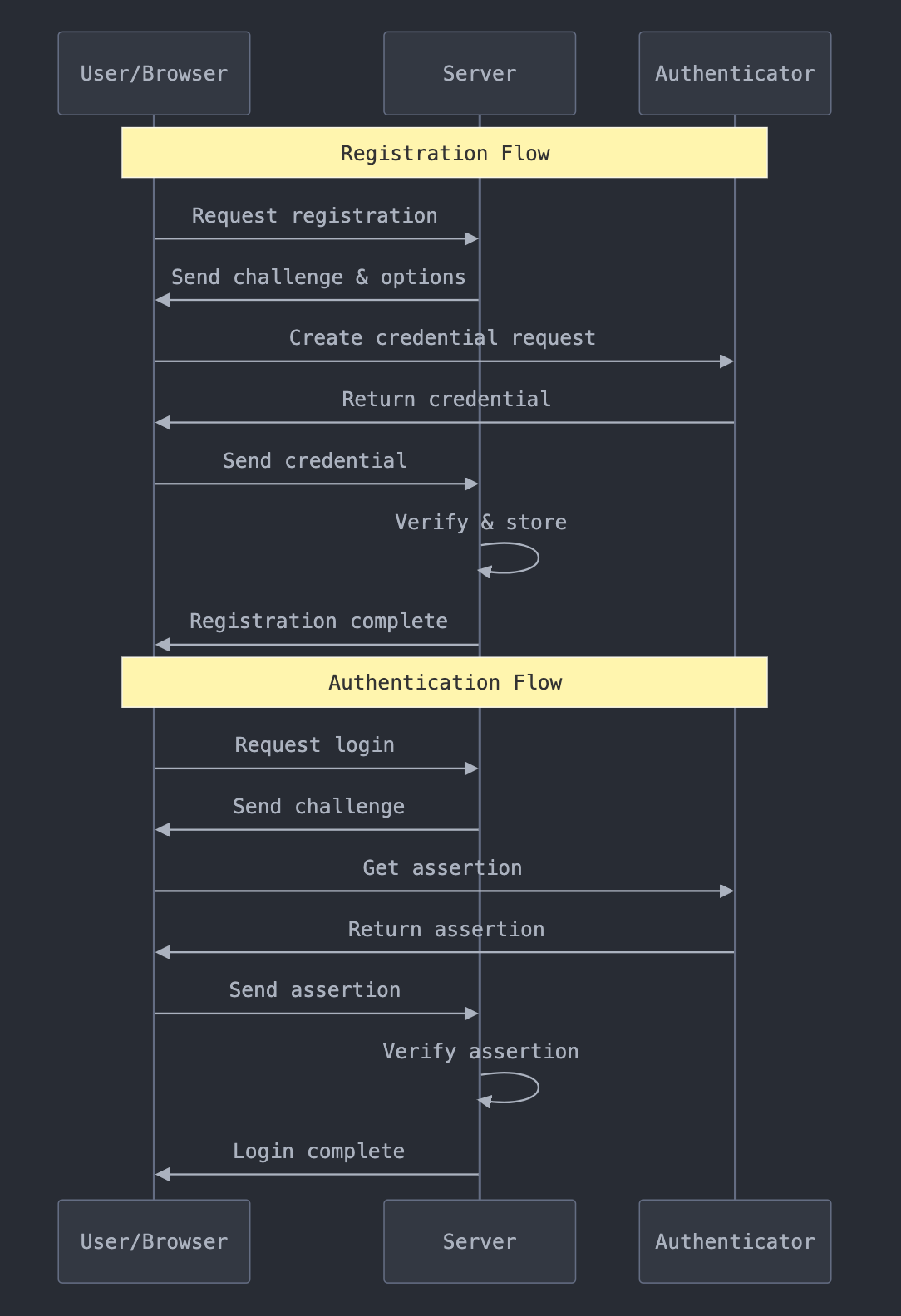
Implementation Overview
Here's what we'll build:
- User registration with FIDO2 credentials
- Passwordless login using those credentials
- Secure session management
What You'll Need
// Required packages for Node.js
npm install fido2-lib express body-parser
Hardware Requirements
- Authenticator Devices: FIDO2-compatible security keys (e.g., YubiKey 5 Series) or biometric devices like fingerprint scanners.
- Development Machine: A computer capable of running a web server and accessing the internet.
- Test Devices: Multiple browsers and devices for cross-platform testing.
Software Requirements
- Programming Language: Knowledge of JavaScript for client-side and a server-side language like Node.js, Python, or Java.
- Web Server: Apache, Nginx, or any server capable of handling HTTPS requests.
- Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, or any database for storing user credentials.
- Libraries and Frameworks:
- Client-Side: Support for the WebAuthn API.
- Server-Side: FIDO2 server libraries compatible with your programming language.
Dependencies and Tools
- SSL Certificates: HTTPS is required for WebAuthn.
- Browser Support: Latest versions of Chrome, Firefox, Edge, or Safari.
- Development Tools: Code editor (e.g., Visual Studio Code), Postman for API testing.
Basic Architecture
┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ Browser │ ←──► │ Server │ ←──► │ Database │
│ (WebAuthn) │ │ (FIDO2Lib) │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
└──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ └──────────────┘
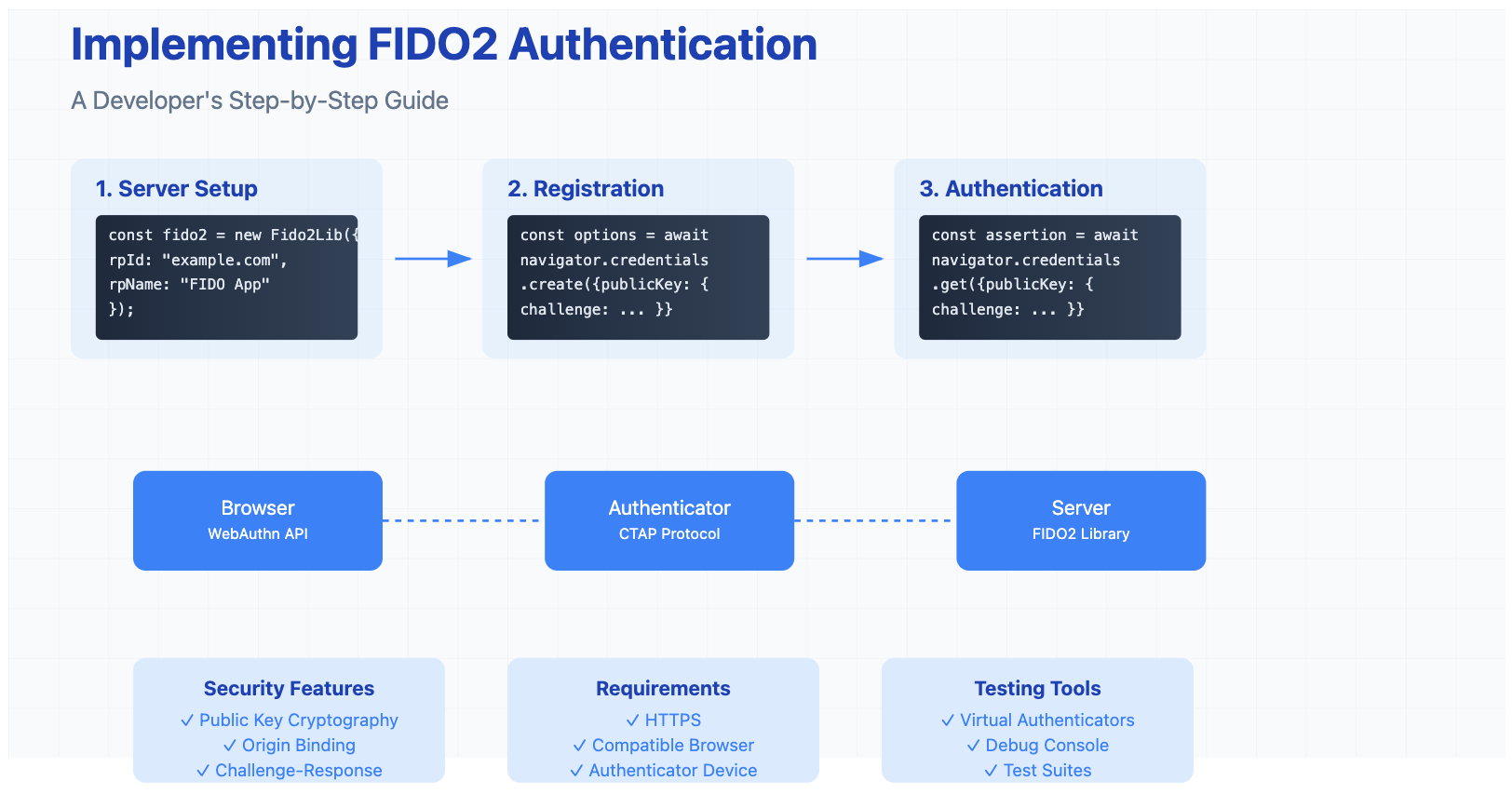
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Server Setup
First, let's set up our Express server with FIDO2 capabilities:
const express = require('express');
const { Fido2Lib } = require('fido2-lib');
const app = express();
// Initialize FIDO2
const f2l = new Fido2Lib({
timeout: 60000,
rpId: "example.com",
rpName: "FIDO Example App",
challengeSize: 32,
attestation: "none"
});
app.use(express.json());
2. Registration Endpoint
Create an endpoint to start the registration process:
app.post('/auth/register-begin', async (req, res) => {
try {
const user = {
id: crypto.randomBytes(32),
name: req.body.username,
displayName: req.body.displayName
};
const registrationOptions = await f2l.attestationOptions();
// Add user info to the options
registrationOptions.user = user;
registrationOptions.challenge = Buffer.from(registrationOptions.challenge);
// Store challenge for verification
req.session.challenge = registrationOptions.challenge;
req.session.username = user.name;
res.json(registrationOptions);
} catch (error) {
res.status(400).json({ error: error.message });
}
});
3. Client-Side Registration
Here's the frontend JavaScript to handle registration:
async function registerUser() {
// 1. Get registration options from server
const response = await fetch('/auth/register-begin', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ username: 'user@example.com' })
});
const options = await response.json();
// 2. Create credentials using WebAuthn
const credential = await navigator.credentials.create({
publicKey: {
...options,
challenge: base64ToBuffer(options.challenge),
user: {
...options.user,
id: base64ToBuffer(options.user.id)
}
}
});
// 3. Send credentials to server
await fetch('/auth/register-complete', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({
id: credential.id,
rawId: bufferToBase64(credential.rawId),
response: {
attestationObject: bufferToBase64(
credential.response.attestationObject
),
clientDataJSON: bufferToBase64(
credential.response.clientDataJSON
)
}
})
});
}
// Helper functions
function bufferToBase64(buffer) {
return btoa(String.fromCharCode(...new Uint8Array(buffer)));
}
function base64ToBuffer(base64) {
return Uint8Array.from(atob(base64), c => c.charCodeAt(0));
}
4. Authentication Flow
Server-side authentication endpoint:
app.post('/auth/login-begin', async (req, res) => {
try {
const assertionOptions = await f2l.assertionOptions();
// Get user's registered credentials from database
const user = await db.getUser(req.body.username);
assertionOptions.allowCredentials = user.credentials.map(cred => ({
id: cred.credentialId,
type: 'public-key'
}));
req.session.challenge = assertionOptions.challenge;
req.session.username = req.body.username;
res.json(assertionOptions);
} catch (error) {
res.status(400).json({ error: error.message });
}
});
Client-side authentication:
async function loginUser() {
// 1. Get authentication options
const response = await fetch('/auth/login-begin', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ username: 'user@example.com' })
});
const options = await response.json();
// 2. Get assertion from authenticator
const assertion = await navigator.credentials.get({
publicKey: {
...options,
challenge: base64ToBuffer(options.challenge),
allowCredentials: options.allowCredentials.map(cred => ({
...cred,
id: base64ToBuffer(cred.id)
}))
}
});
// 3. Verify with server
await fetch('/auth/login-complete', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({
id: assertion.id,
rawId: bufferToBase64(assertion.rawId),
response: {
authenticatorData: bufferToBase64(
assertion.response.authenticatorData
),
clientDataJSON: bufferToBase64(
assertion.response.clientDataJSON
),
signature: bufferToBase64(
assertion.response.signature
)
}
})
});
}
Common Challenges & Solutions
1. Browser Compatibility
// Check if WebAuthn is supported
if (!window.PublicKeyCredential) {
console.log('WebAuthn not supported');
// Fall back to traditional authentication
return;
}
// Check if user verifying platform authenticator is available
const available = await PublicKeyCredential.isUserVerifyingPlatformAuthenticatorAvailable();
if (!available) {
console.log('Platform authenticator not available');
// Consider security key instead
}
2. Error Handling
// Client-side error handling
try {
const credential = await navigator.credentials.create({/*...*/});
} catch (error) {
switch (error.name) {
case 'NotAllowedError':
console.log('User declined to create credential');
break;
case 'SecurityError':
console.log('Origin not secure');
break;
default:
console.error('Unknown error:', error);
}
}
3. Base64 URL Encoding
function base64UrlEncode(buffer) {
const base64 = bufferToBase64(buffer);
return base64.replace(/\+/g, '-')
.replace(/\//g, '_')
.replace(/=/g, '');
}
Testing Your Implementation
1. Basic Test Suite
describe('FIDO2 Authentication', () => {
it('should generate registration options', async () => {
const response = await fetch('/auth/register-begin', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ username: 'test@example.com' })
});
const options = await response.json();
expect(options).toHaveProperty('challenge');
expect(options).toHaveProperty('rp');
expect(options.rp.name).toBe('FIDO Example App');
});
});
2. Virtual Authenticator Testing
// Using Chrome's Virtual Authenticator Environment
const virtualAuthenticatorOptions = {
protocol: 'ctap2',
transport: 'internal',
hasResidentKey: true,
hasUserVerification: true,
isUserConsenting: true
};
const authenticator = await driver.addVirtualAuthenticator(
virtualAuthenticatorOptions
);
Security Best Practices
- Always Use HTTPS
if (window.location.protocol !== 'https:') {
throw new Error('FIDO2 requires HTTPS');
}
- Validate Origin
const expectedOrigin = 'https://example.com';
const clientDataJSON = JSON.parse(
new TextDecoder().decode(credential.response.clientDataJSON)
);
if (clientDataJSON.origin !== expectedOrigin) {
throw new Error('Invalid origin');
}
- Challenge Verification
if (!timingSafeEqual(
storedChallenge,
credential.response.challenge
)) {
throw new Error('Challenge mismatch');
}
Production Checklist
✅ HTTPS configured
✅ Error handling implemented
✅ Browser support detection
✅ Backup authentication method
✅ Rate limiting enabled
✅ Logging system in place
✅ Security headers configured
Next Steps
- Implement user presence verification
- Add transaction confirmation
- Set up backup authentication methods
- Configure audit logging
- Implement rate limiting
Resources:
Need help? Join Discord community for support.

