The Future of Cybersecurity: Global Outlook 2025 and Beyond
The cybersecurity landscape is entering an unprecedented era of complexity, with AI-driven threats, geopolitical tensions, and supply chain vulnerabilities reshaping how organizations approach digital security. This analysis explores key trends and strategic imperatives for 2025 and beyond.
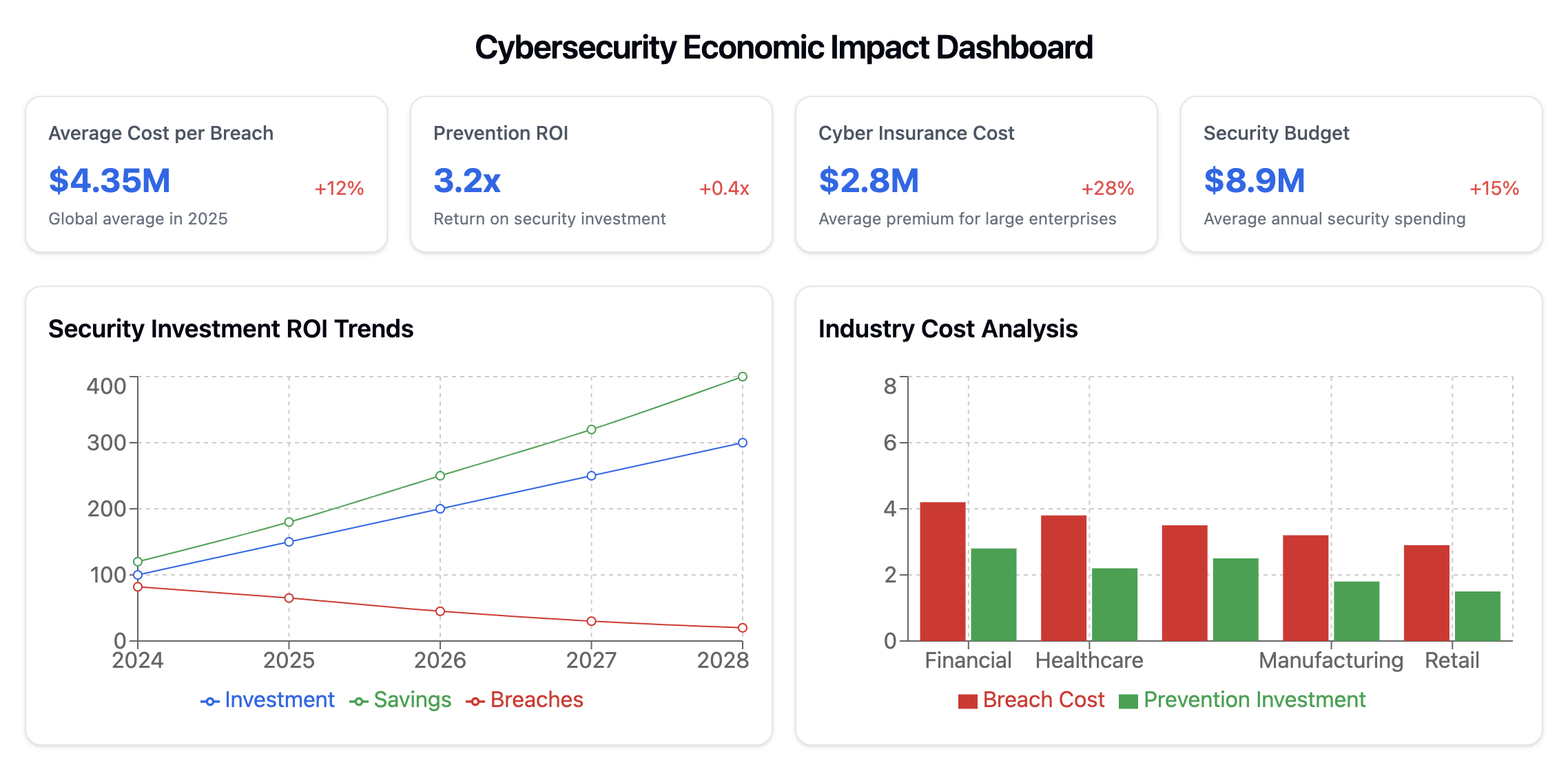
The cybersecurity landscape is entering an unprecedented era of complexity, marked by converging challenges that are fundamentally reshaping how organizations approach digital security. The World Economic Forum's Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 reveals a critical inflection point where traditional security approaches are being challenged by emerging technologies, geopolitical tensions, and evolving threat landscapes.
The New Complexity Paradigm
According to the WEF report, six key factors are driving increasing complexity in cybersecurity:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Nearly 60% of organizations report that their cybersecurity strategies are directly influenced by geopolitical uncertainties. This has led to 18% of organizations adjusting their trading policies and 17% halting operations in certain regions entirely.
- AI and Emerging Technologies: While 66% of organizations expect AI to significantly impact cybersecurity, only 37% have processes in place to assess AI security risks before deployment, creating a dangerous gap in preparedness.
- Supply Chain Interdependencies: 54% of large organizations identify supply chain challenges as their greatest barrier to achieving cyber resilience, highlighting the growing complexity of securing interconnected business ecosystems.
- Regulatory Requirements: The proliferation of cybersecurity regulations worldwide, while beneficial for baseline security, is creating significant compliance challenges. Over 76% of CISOs report that regulatory fragmentation affects their ability to maintain compliance.
- Cybercrime Sophistication: 72% of organizations report increased cyber risks, with ransomware remaining a top concern. Adversarial advances powered by generative AI are enabling more sophisticated and scalable attacks.
- Skills Gap: The cybersecurity workforce shortage has widened by 8% since 2024, with two out of three organizations reporting moderate-to-critical skills gaps.
Emerging Threats and Vulnerabilities
The Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 identifies several critical emerging threat vectors that are reshaping the cybersecurity landscape. These threats are characterized by their increasing sophistication, broader impact potential, and the challenges they present to traditional security approaches.
Critical Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
Water Systems and Utilities
Recent attacks on water infrastructure have exposed critical vulnerabilities in essential services. The report highlights a concerning trend where attackers are specifically targeting water treatment and distribution systems:
- Control system manipulation risks have increased by 46% since 2024
- Remote access vulnerabilities remain a primary attack vector
- Legacy system dependencies create persistent security gaps
- Cascade effects can impact multiple dependent infrastructure systems
The report notes that water facility attacks have evolved from primarily disruptive incidents to sophisticated attempts at contamination and systemic damage, representing a significant escalation in threat severity.
Energy Grid Infrastructure
The energy sector faces unique challenges due to the convergence of operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT):
- State-sponsored attacks on power distribution systems have increased by 72%
- Solar and wind farm control systems present new attack surfaces
- Smart grid technologies introduce additional vulnerability points
- Energy storage systems are emerging as potential targets
The integration of renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies is creating new security challenges that many organizations are not fully prepared to address.
Healthcare Systems
Healthcare infrastructure has emerged as a primary target, with attacks becoming more sophisticated and harmful:
- Medical device vulnerabilities have increased by 38%
- Ransomware attacks specifically targeting patient care systems are up 57%
- AI-driven attacks on diagnostic systems represent a new threat vector
- Supply chain attacks affecting pharmaceutical manufacturing have doubled
Emerging Technology Threats
Quantum Computing Risks
The report identifies quantum computing as a looming threat to current cryptographic systems:
- 40% of organizations have begun assessing quantum threats
- "Store now, decrypt later" attacks are increasing
- Current encryption standards face obsolescence within 5-7 years
- Quantum-resistant cryptography adoption remains low at 12%
AI-Driven Threats
The AI security paradox represents a fundamental shift in the threat landscape:
- Large Language Model (LLM) manipulation for social engineering
- AI-powered zero-day vulnerability discovery
- Automated attack customization and scaling
- Deepfake-enhanced business email compromise attacks
- AI model poisoning and evasion techniques
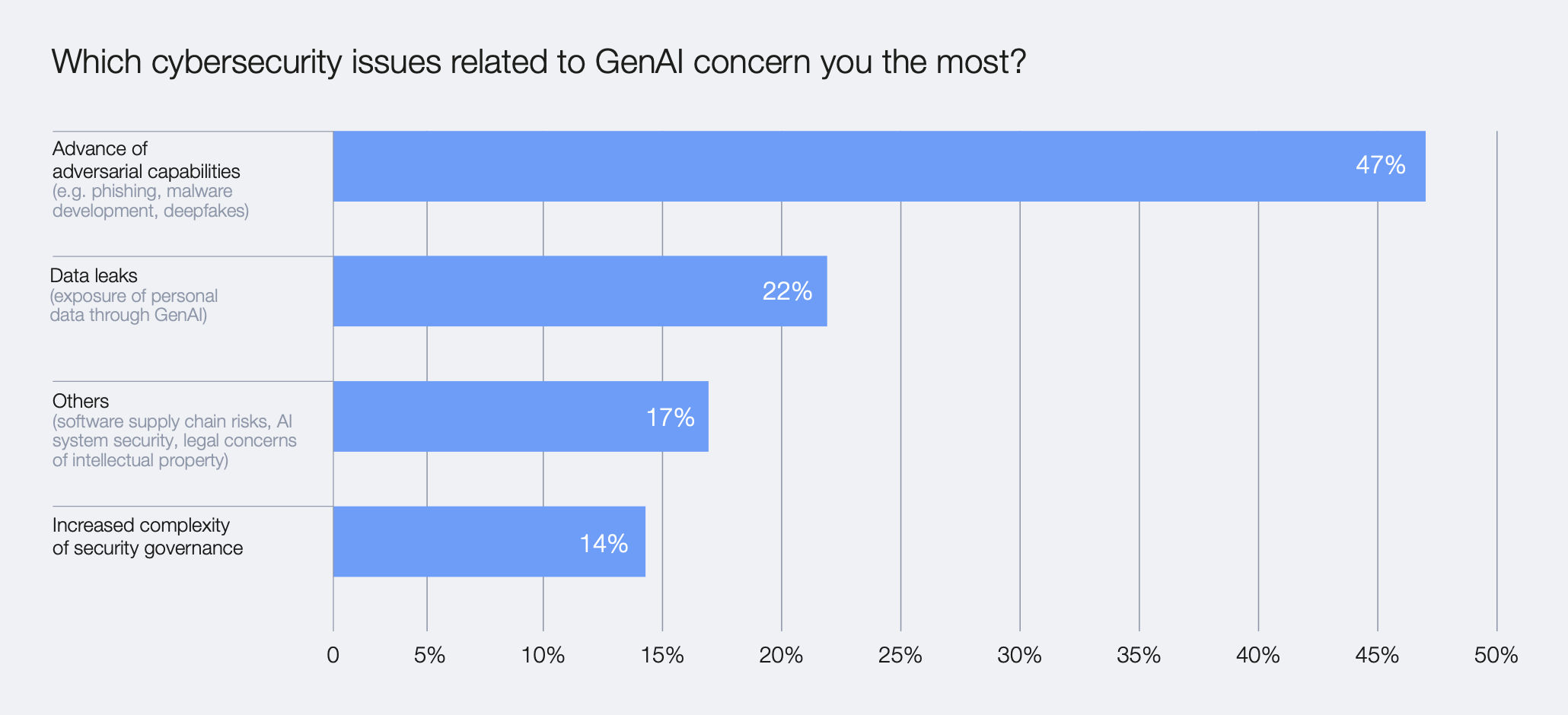
The report notes that 47% of organizations cite adversarial AI capabilities as their primary concern for 2025.
Biosecurity and Digital Systems
The convergence of biological and digital systems presents unprecedented risks:
- Laboratory system compromises could affect genetic research
- Digital bio-data theft poses privacy and security risks
- Automated laboratory systems face increasing attack attempts
- Biomedical device vulnerabilities can directly impact patient safety
The WHO has warned that AI and cyber attacks could pose catastrophic risks to global biosecurity by 2026.
Communication Infrastructure
Space-Based Systems
Satellite and space-based communication systems face growing threats:
- 124 recorded cyber operations against space infrastructure in 2024
- GPS spoofing incidents have increased by 85%
- Satellite communication jamming poses risks to critical services
- Space-based internet services face new types of denial-of-service attacks
Undersea Infrastructure
Submarine communication cables and systems are increasingly vulnerable:
- Physical and cyber attacks on undersea cables have increased
- New methods of cable system compromise are emerging
- Limited redundancy in certain regions increases risk
- State-sponsored threats to undersea infrastructure are growing
Supply Chain and Ecosystem Threats
The report emphasizes the growing complexity of supply chain attacks:
- Third-party software compromises have increased by 54%
- Cloud service provider dependencies create new risks
- Software supply chain attacks have become more sophisticated
- Open-source component vulnerabilities remain a significant concern
Emerging Social Engineering Threats
Social engineering attacks have evolved significantly:
- AI-generated phishing campaigns show 300% higher success rates
- Voice cloning attacks have increased by 250%
- Deepfake-based fraud has caused $1.2 billion in losses
- Multi-channel social engineering attacks are becoming common
Financial System Threats
New threats to financial systems are emerging:
- Cryptocurrency infrastructure attacks have increased
- Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) systems face new threats
- Payment system vulnerabilities are being actively exploited
- Cross-border financial system attacks are growing in frequency
The report emphasizes that these threats are not isolated but often interconnected, creating complex risk scenarios that organizations must prepare for. The convergence of multiple threat vectors, combined with the rapid pace of technological change, requires a fundamental shift in how organizations approach security and risk management.
Opportunities and Strategic Imperatives
The evolving cybersecurity landscape, while presenting significant challenges, also creates unprecedented opportunities for organizations to transform their security posture and create competitive advantages. The Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 identifies several key areas where organizations can leverage emerging trends and technologies to enhance their security capabilities.
Building Resilient Ecosystems
The report emphasizes that ecosystem resilience has become a critical differentiator for successful organizations. This presents several opportunities:
Collaborative Defense Networks
Organizations can establish and participate in industry-specific threat sharing networks. The report indicates that organizations participating in such networks demonstrate 43% better threat detection rates and 27% faster incident response times. Key components include:
- Real-time threat intelligence sharing platforms
- Cross-industry incident response teams
- Shared security operations centers
- Joint tabletop exercises and scenario planning
- Collaborative security research and development
Supply Chain Innovation
The complexity of supply chain security is driving innovative approaches to risk management:
- Implementation of blockchain for supply chain transparency
- Development of automated supplier security assessment tools
- Creation of shared security standards and frameworks
- Establishment of industry-wide security certification programs
- Integration of AI-driven supply chain risk monitoring
The report notes that organizations implementing these innovations have reduced supply chain incidents by 35% on average.
AI and Automation Opportunities
Defensive AI Applications
The report identifies several promising areas for AI application in security:
- Automated threat hunting and detection
- Predictive security analytics
- Intelligent security orchestration
- Natural language processing for threat intelligence
- Behavioral analysis and anomaly detection
Organizations effectively implementing defensive AI have seen:
- 67% reduction in false positive alerts
- 41% improvement in threat detection speed
- 53% decrease in incident response time
- 38% reduction in security operational costs
Security Process Automation
Process automation presents significant opportunities for efficiency and effectiveness:
- Security operations automation
- Compliance monitoring and reporting
- Vulnerability management
- Access control and identity management
- Incident response and recovery
The report indicates that automation of routine security tasks can free up to 30% of security team capacity for more strategic activities.
Workforce Development Innovation
The cybersecurity skills gap is driving creative solutions in workforce development:
AI-Augmented Security Teams
Organizations are finding success with hybrid human-AI security teams:
- AI assistants for tier-1 security operations
- Automated threat analysis and triage
- Machine learning-powered decision support
- Intelligent security training systems
- AI-driven security documentation and knowledge management
Novel Training Approaches
Innovative training methods are showing promising results:
- Virtual reality security training environments
- Gamified learning platforms
- AI-personalized learning pathways
- Hands-on cyber ranges
- Peer-to-peer learning networks
Organizations implementing these approaches report a 45% improvement in security team effectiveness and a 60% reduction in training time.
Economic Opportunities
The report identifies several areas where organizations can create economic value through security:
Security as a Business Enabler
Organizations can leverage security capabilities to:
- Create competitive differentiation
- Enable new business models
- Accelerate digital transformation
- Enhance customer trust
- Drive operational efficiency
New Market Opportunities
Emerging security needs are creating new markets:
- Security-as-a-Service offerings
- Specialized security consulting
- Compliance automation tools
- Security training and certification
- Risk transfer and insurance products
Regulatory Compliance as Opportunity
While regulatory compliance presents challenges, it also creates opportunities:
Standardization Benefits
- Reduced complexity through common frameworks
- Improved inter-organizational collaboration
- Clear security investment justification
- Enhanced stakeholder trust
- Simplified vendor assessment
Innovation Drivers
Regulations are driving security innovation in:
- Privacy-enhancing technologies
- Security monitoring and reporting tools
- Identity and access management solutions
- Data protection technologies
- Compliance automation platforms
Strategic Technology Integration
The report emphasizes opportunities in emerging technology integration:
Zero Trust Architecture
Organizations implementing zero trust architectures report:
- 76% reduction in breach impact
- 43% improvement in application security
- 38% reduction in security complexity
- 29% decrease in security costs
Quantum-Safe Security
Early movers in quantum-safe security are:
- Developing competitive advantages
- Securing long-term data protection
- Building quantum-resistant infrastructures
- Creating new service offerings
- Establishing industry leadership
The report emphasizes that success in leveraging these opportunities requires a balanced approach that considers both immediate needs and long-term strategic objectives. Organizations must also maintain flexibility to adapt their strategies as new opportunities emerge and the security landscape continues to evolve.
Future Outlook (2025-2030)
The report projects several key developments:

- Autonomous Security Systems: By 2027, fully autonomous security systems capable of detecting, analyzing, and responding to threats without human intervention will become mainstream.
- Quantum-Ready Infrastructure: Organizations must begin transitioning to quantum-resistant cryptography by 2028-2029.
- Zero-Trust Evolution: Advanced behavioral biometrics and AI-driven trust scoring will become standard components of security architectures.
- Regulatory Convergence: Efforts to harmonize international cybersecurity regulations will accelerate, though challenges will persist.
Recommendations for Organizations
The increasing complexity of the cybersecurity landscape demands a comprehensive and structured approach to organizational security. Based on the Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025, organizations should focus on the following key areas:
1. AI Security Integration and Governance
Organizations must develop robust frameworks for AI security that include:
- Comprehensive pre-deployment security assessments for all AI tools and systems
- Continuous monitoring mechanisms for AI model behavior and outputs
- Clear protocols for AI incident response and model adjustment
- Regular audits of AI system decisions and security impacts
- Integration of AI security considerations into broader risk management frameworks
The report emphasizes that organizations should establish dedicated AI governance committees that include representation from security, legal, and business units to ensure balanced decision-making in AI deployment.
2. Ecosystem Resilience and Supply Chain Security
Building resilience requires looking beyond organizational boundaries to include:
- Implementation of real-time supply chain monitoring systems
- Development of collaborative threat intelligence sharing networks
- Creation of joint incident response plans with key suppliers and partners
- Regular assessment and validation of third-party security controls
- Implementation of zero-trust architectures that account for ecosystem dependencies
According to the report, organizations should allocate at least 15% of their security budget to ecosystem-wide initiatives and collaborative security measures.
3. Human Capital Development
The widening skills gap requires a multi-faceted approach to workforce development:
- Creation of internal cybersecurity academies and training programs
- Implementation of mentor-mentee programs to accelerate knowledge transfer
- Development of cross-functional security awareness programs
- Investment in AI-assisted tools to augment human capabilities
- Establishment of clear cybersecurity career paths and progression frameworks
The report indicates that organizations with strong human capital development programs show 40% better resilience against sophisticated attacks.
4. Economic Framework Implementation
Organizations should adopt quantitative approaches to security that include:
- Development of cyber risk quantification models
- Implementation of return-on-security-investment (ROSI) calculations
- Creation of security metrics tied to business outcomes
- Integration of cybersecurity considerations into business strategy
- Regular board-level reporting on security economics and risk exposure
5. Operational Resilience Enhancement
Building operational resilience requires:
- Regular testing of business continuity and disaster recovery plans
- Implementation of automated security orchestration and response
- Development of scenario-based incident response playbooks
- Creation of crisis communication protocols
- Regular cyber crisis exercises involving senior leadership
6. Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Organizations must develop structured approaches to managing compliance that include:
- Creation of centralized compliance monitoring systems
- Development of automated compliance reporting capabilities
- Implementation of privacy-by-design principles
- Regular assessment of regulatory changes and their impacts
- Integration of compliance requirements into security architecture
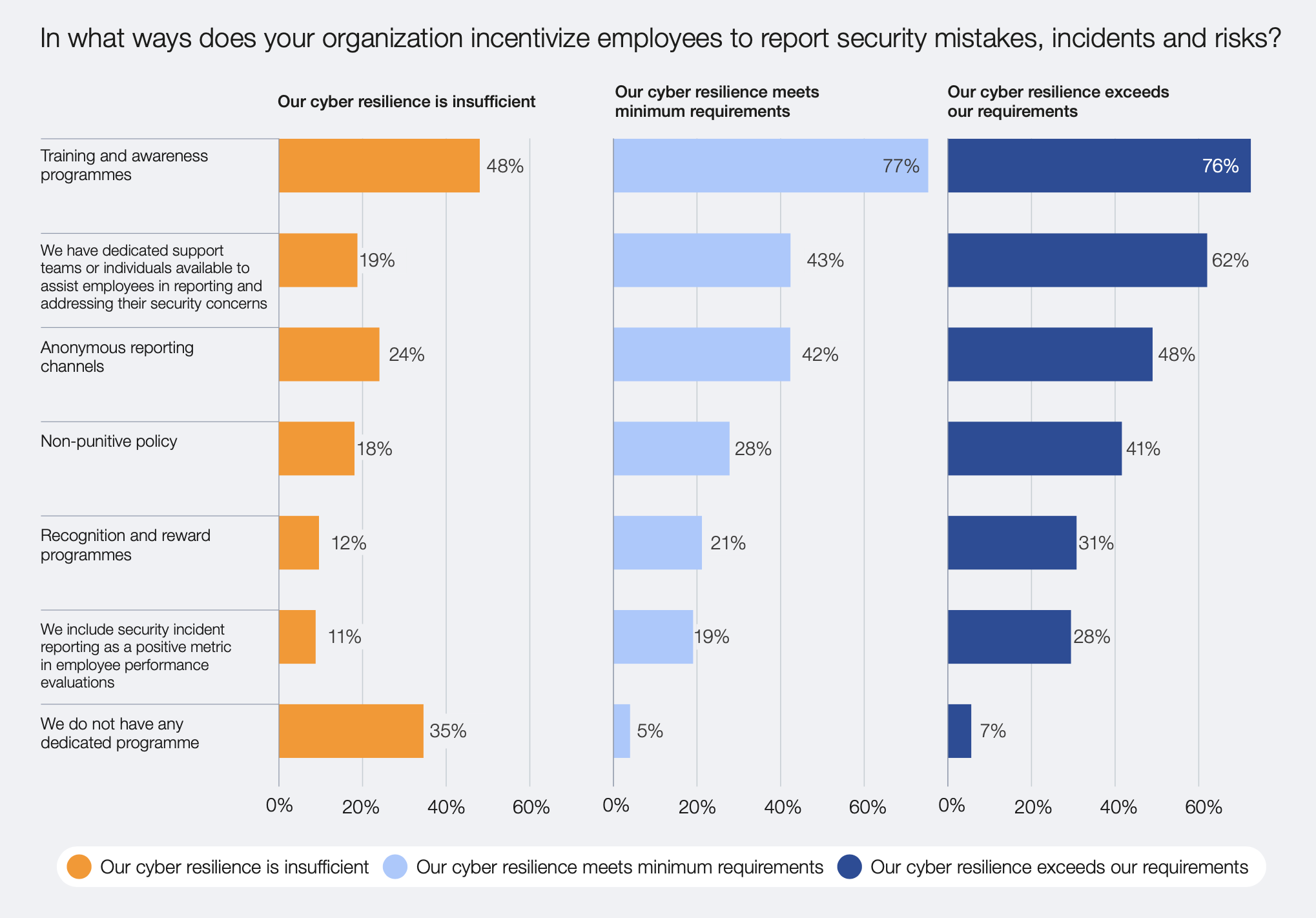
7. Security Culture Development
Building a strong security culture requires:
- Regular security awareness training and simulations
- Recognition programs for security-conscious behavior
- Clear communication of security policies and expectations
- Integration of security considerations into performance evaluations
- Development of security champions across business units
8. Technology Innovation Management
Organizations should establish frameworks for managing security in technological innovation:
- Creation of security requirements for new technology adoption
- Implementation of secure development lifecycles
- Regular security testing of new technologies
- Integration of security considerations into digital transformation initiatives
- Development of technology risk assessment frameworks
Implementation Priorities
The report suggests organizations should prioritize these recommendations based on:
- Current security maturity level
- Industry-specific threat landscape
- Regulatory requirements
- Available resources and capabilities
- Business strategic objectives
Conclusion
The Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 paints a picture of both challenge and opportunity. While the complexity of threats continues to grow, organizations that adopt proactive, collaborative approaches to security while leveraging emerging technologies thoughtfully will be best positioned to thrive in this new era.
Success will require not just technological solutions but a fundamental shift in how organizations approach security - moving from isolated defensive postures to collaborative, ecosystem-wide resilience strategies. The report suggests that 2025 represents a critical year for organizations to make this transition, as the convergence of AI, geopolitical tensions, and evolving threats creates both unprecedented risks and opportunities for innovation in cybersecurity.
Read and download the complete report:

