The Enterprise Readiness Playbook: Transform Your B2B SaaS from Startup to Enterprise-Grade
Discover the comprehensive roadmap for B2B SaaS companies to achieve enterprise readiness. Learn essential infrastructure requirements, compliance frameworks, enterprise features, and go-to-market strategies from a serial founder who scaled through product-led growth.
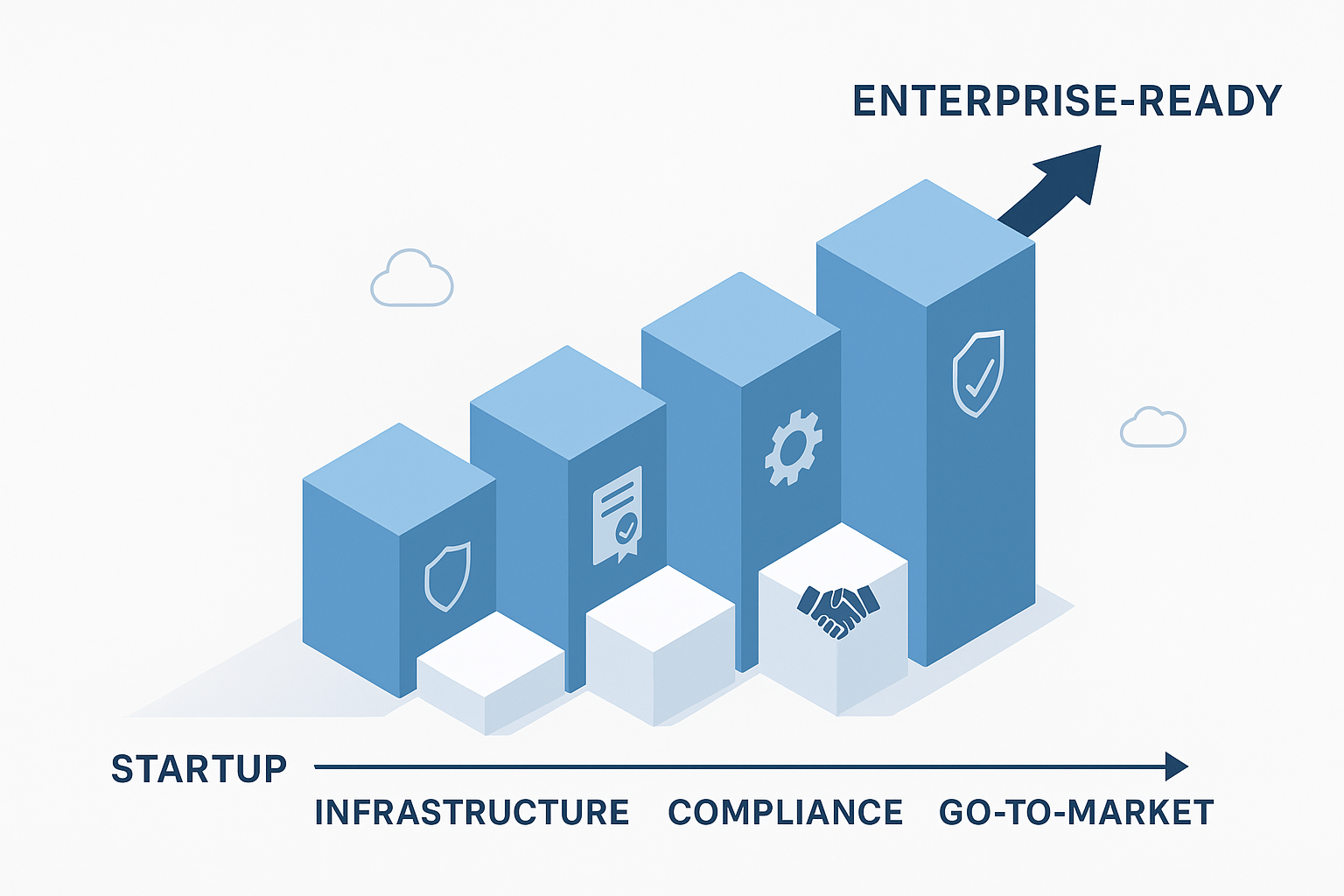
The journey from serving SMBs to enterprise customers represents a significant evolution for B2B SaaS companies—one that demands fundamental changes across your entire organization. This comprehensive guide provides a strategic framework for achieving enterprise readiness, covering critical infrastructure requirements, compliance certifications, feature development priorities, and go-to-market adjustments. Drawing from hands-on experience scaling a cybersecurity SaaS platform, this playbook offers practical guidance for founders and product leaders navigating this complex transition.
The Enterprise Opportunity (and Challenge)
Enterprise customers can transform your business trajectory with larger contracts, longer commitments, and strategic partnerships. However, they also bring heightened expectations for security, reliability, compliance, and customer support that many growing B2B companies aren't prepared to meet.
Having guided a cybersecurity SaaS business from early-stage to enterprise-ready, I've learned that enterprise readiness isn't just about checking boxes on a procurement form—it's a comprehensive evolution of how you build, secure, sell, and support your product. Let's explore what it takes to make this transformation successfully.
1. Enterprise-Ready Infrastructure Requirements
Security Architecture: Embracing Zero-Trust
Enterprise customers expect security to be foundational, not an afterthought. Building a zero-trust architecture should be your north star, implementing the principle of "never trust, always verify" across your infrastructure.
In my experience scaling a digital identity platform, I found that enterprise buyers wouldn't even begin technical evaluations until we could demonstrate:
- Network segmentation: Micro-segmentation of your infrastructure to contain potential breaches
- Continuous verification: Authentication that extends beyond the perimeter with continuous session validation
- Least privilege access: Strict limitations on who can access what, even for your internal team
- Comprehensive monitoring: Visibility across all infrastructure, with alerting on anomalous patterns
- Encryption everywhere: Both in transit and at rest, with proper key management
A common mistake is implementing these controls superficially for compliance checklists rather than as core architectural principles. When we embedded zero-trust principles into our engineering culture—including security reviews in sprint planning and regular penetration testing—our enterprise sales cycles shortened dramatically.
Scalability and Reliability Benchmarks
Enterprise customers expect five nines (99.999%) reliability and seamless scaling, even if they rarely state it explicitly. In practice, this requires:
- Robust SLAs: Clearly defined and measurable service level agreements with financial consequences
- Geographic redundancy: Distributed infrastructure across multiple regions
- Auto-scaling architecture: Systems that expand capacity during usage spikes
- Load testing protocols: Regular testing of how systems perform under stress
- Disaster recovery planning: Documented and tested recovery processes with aggressive RTOs/RPOs
When we identified reliability as a primary enterprise blocker, we invested in reshaping our infrastructure from a monolithic to microservices architecture. This wasn't a superficial change—it required retraining engineers, establishing new monitoring practices, and implementing chaos engineering to proactively identify weaknesses.
Identity Management and Access Control
For enterprise customers, sophisticated identity management isn't a feature—it's mandatory infrastructure. Your system should support:
- Enterprise SSO integration: Support for SAML, OAuth, and OIDC with major identity providers
- Multi-factor authentication: Multiple options for secondary verification
- Role-based access control: Granular permissions that map to organizational hierarchies
- Just-in-time access: Temporary elevated permissions with approval workflows
- Directory synchronization: Automated user provisioning and deprovisioning
When we made our RBAC system more flexible and introduced custom roles to accommodate complex organizational structures, our enterprise adoption accelerated significantly. The lesson: identity capabilities that seem excessive for SMB customers become table stakes for enterprises.
2. Critical Compliance and Certification Roadmap
Industry-Specific Compliance Requirements
Enterprise compliance requirements vary by industry, but most enterprise customers will expect:
- SOC 2 Type II: The baseline security framework for most SaaS providers
- ISO 27001: Increasingly required, especially for international customers
- GDPR compliance: Mandatory for processing EU citizen data
- Industry-specific frameworks: HIPAA for healthcare, PCI DSS for payments, FedRAMP for government
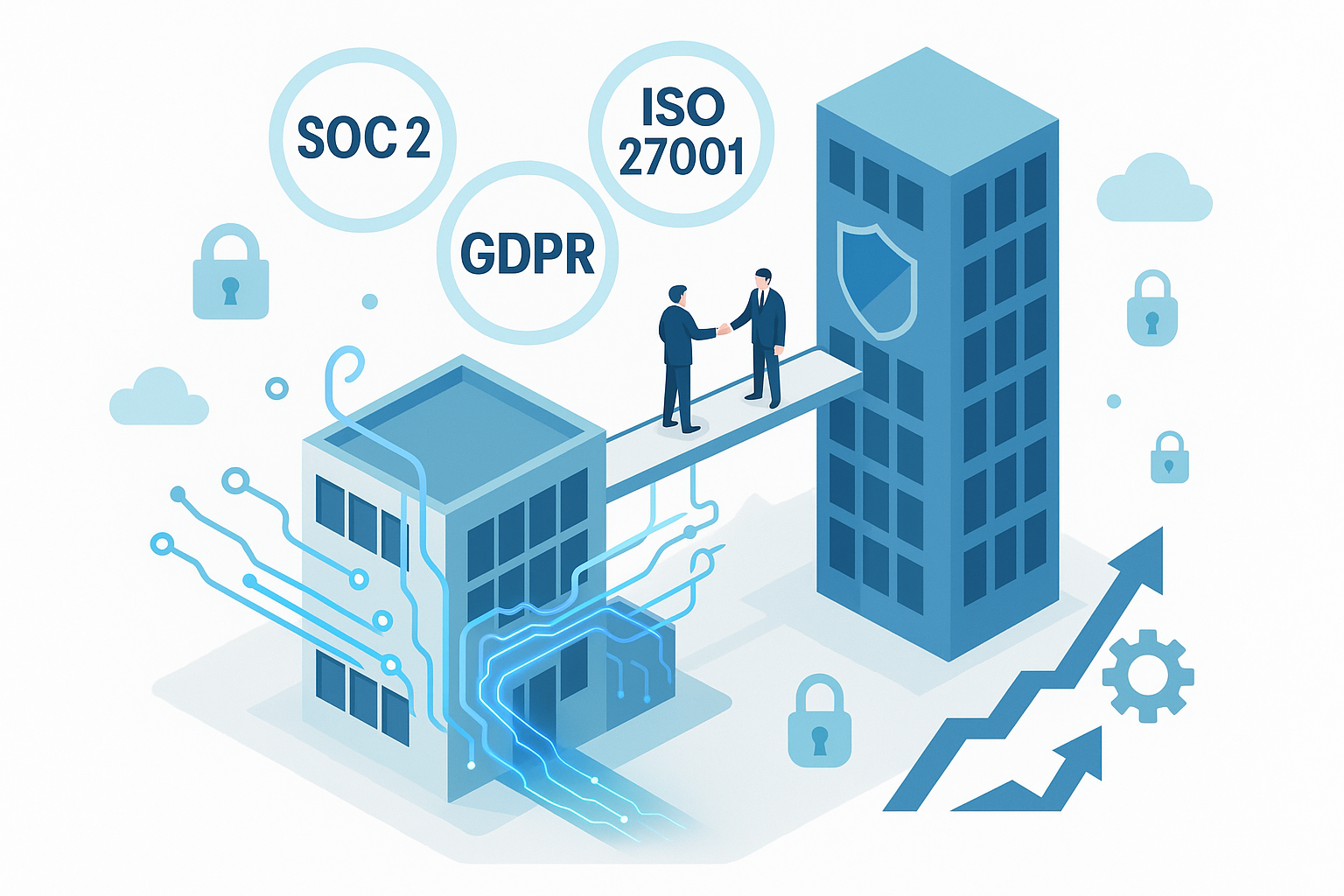
Rather than viewing compliance as a checkbox exercise, successful enterprise-ready companies integrate compliance requirements into their development lifecycle. When we embedded security and compliance requirements into our sprint planning, we transformed compliance from a bottleneck into a competitive advantage.
Documentation and Evidence Collection
The difference between claiming compliance and proving compliance often determines enterprise deal success. Establish:
- Evidence collection automation: Tools that gather compliance artifacts automatically
- Centralized evidence repository: A single source of truth for all compliance documentation
- Policy management system: Version-controlled policies that reflect actual practices
- Vendor risk management: Assessment and monitoring of your own suppliers
- Regular attestation processes: Scheduled reviews of controls effectiveness
When enterprise prospects requested evidence during security reviews, our ability to provide comprehensive documentation within hours rather than weeks dramatically accelerated our sales cycles.
Practical Implementation Timeline
Achieving comprehensive compliance isn't an overnight process. A realistic timeline for a growing B2B SaaS company:
- Months 1-3: Gap assessment and policy development
- Months 3-6: Control implementation and evidence collection processes
- Months 6-9: Initial audit preparation and remediation
- Months 9-12: First audit cycles and certification
- Ongoing: Continuous monitoring and improvement
This timeline requires dedicated resources—when we appointed a full-time compliance manager rather than distributing responsibilities across already-busy team members, our compliance velocity increased substantially.
3. Enterprise-Grade Feature Development
User Management and Role-Based Access Control
Enterprise customers manage hundreds or thousands of users with complex organizational structures. Your product must support:
- Hierarchical user management: Organizations, divisions, teams, and individual users
- Custom role definitions: Beyond basic admin/user dichotomies
- Permission inheritance: Logical propagation of access rights
- User activity reporting: Comprehensive usage analytics by role and individual
- Delegation capabilities: Allowing enterprise admins to manage their domains
When we expanded our role system from three predefined roles to custom role creation with granular permissions, our enterprise adoption increased dramatically—customers could finally map our software to their organizational structures.
Audit Logging and Activity Monitoring
For compliance and security, enterprises need comprehensive visibility into system activity:
- Immutable audit logs: Tamper-evident records of all system actions
- User session recordings: The ability to replay user actions for investigation
- Anomaly detection: Alerting on unusual patterns or potential security events
- Log retention policies: Configurable retention periods that meet compliance requirements
- Export capabilities: The ability to integrate logs with enterprise SIEM systems
Implementing detailed audit logging not only satisfied enterprise requirements but also reduced our support burden—customers could often self-serve answers to "who did what and when" questions that previously required support tickets.
Advanced Security Features and Customization
Enterprise security teams expect configuration flexibility beyond what SMB customers typically require:
- Custom password policies: Allowing alignment with corporate standards
- IP restrictions: Limiting access to approved networks
- Session management: Controls for timeout, concurrent sessions, and device limitations
- Data residency options: Controlling where customer data is stored and processed
- Custom encryption: Supporting customer-managed keys and encryption standards
When we introduced advanced security configuration options, we discovered that many enterprise customers had specific requirements that weren't in our product roadmap. Providing a customization framework with secure defaults proved more effective than trying to anticipate every possible requirement.
4. Go-to-Market Strategy Adjustments
Transitioning from PLG to Enterprise Sales Motions
Product-led growth and enterprise sales aren't mutually exclusive, but they require different approaches:
- Sales-assisted PLG: Adding human touchpoints to the self-service journey
- Value demonstration: Shifting from feature messaging to business outcomes
- ROI calculators: Quantifying the business impact of your solution
- Proof of concept framework: Structured trial programs with success criteria
- Procurement support: Resources for navigating complex buying processes
When we introduced a "white-glove" onboarding option alongside our self-service flow, enterprise adoption accelerated dramatically—customers appreciated the option to self-serve features while having guidance for complex implementations.
Customer Success Infrastructure for Enterprise Clients
Enterprise customers expect dedicated support infrastructure:
- Tiered support offerings: Including premium options with guaranteed response times
- Technical account management: Dedicated resources for strategic customers
- Customer health monitoring: Proactive identification of adoption issues
- Executive business reviews: Quarterly strategic alignment sessions
- Escalation matrices: Clear paths for critical issue resolution
When we implemented a dedicated enterprise support tier with named contacts, our retention rates improved significantly—enterprise customers valued the relationship as much as the technology.
Sales Enablement and Documentation Requirements
Enterprise sales teams need comprehensive resources to navigate complex sales cycles:
- Security whitepapers: Detailed explanations of your security architecture
- Compliance documentation: Certifications and audit reports
- Implementation playbooks: Step-by-step guides for successful deployment
- ROI case studies: Evidence of value delivered to similar organizations
- Competitive battle cards: Positioning against enterprise alternatives
Our most successful enterprise quarter came after we developed comprehensive security documentation that sales teams could share early in the sales process—prospects could self-qualify our security posture before investing in deep technical evaluations.
Conclusion: The Enterprise Readiness Journey
Becoming enterprise-ready isn't a destination but a continuous journey. As enterprise customer expectations evolve, your infrastructure, compliance, features, and go-to-market strategies must evolve as well.
The transition requires substantial investment—in our case, dedicating approximately 30% of engineering resources to enterprise readiness for a full year before seeing significant enterprise revenue. However, the returns justified the investment, with average contract values increasing 5x and sales cycles eventually shortening by 40%.
For B2B SaaS companies looking to make this transition, remember that enterprise readiness is a company-wide transformation, not just a product initiative. It requires alignment across product, engineering, security, sales, marketing, and customer success teams.
Enterprise Readiness Checklist
Infrastructure
- Implemented zero-trust security architecture
- Established 99.9%+ uptime with transparent status page
- Deployed geographic redundancy across multiple regions
- Implemented enterprise-grade identity management
- Established comprehensive monitoring and alerting
Compliance
- Completed SOC 2 Type II certification
- Implemented ISO 27001 controls
- Established GDPR compliance program
- Developed industry-specific compliance frameworks
- Created automated evidence collection processes
Product Features
- Built hierarchical user management
- Implemented custom role-based access control
- Developed comprehensive audit logging
- Created enterprise security configuration options
- Established data residency controls
Go-to-Market
- Developed enterprise-specific pricing tier
- Created technical account management program
- Built security and compliance documentation library
- Established enterprise POC framework
- Implemented executive business review process
By methodically addressing each aspect of this framework, B2B SaaS companies can successfully transition from serving small and mid-sized businesses to capturing the tremendous opportunities in the enterprise market.
About the Author: A serial entrepreneur with a passion for technology, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence. From scaling a cybersecurity SaaS to through product-led growth to developing AI-powered marketing solutions, the author brings hands-on experience in building enterprise-ready B2B platforms.

