Identity's New Frontier: AI, Machines, and the Future of Digital Trust
The identity industry faces its biggest shift yet: machines now outnumber humans 90:1 in digital systems. From AI-powered authentication to passwordless futures, discover the $61.74B transformation reshaping how we think about digital trust and security.

The identity industry stands at its most transformative moment since the advent of digital authentication. At Identiverse 2025 in Las Vegas, over 3,000 cybersecurity professionals witnessed a paradigm shift where non-human identities now outnumber humans by ratios exceeding 90:1, fundamentally reshaping how we think about access, trust, and security in an AI-driven world. This isn't just another technological evolution—it's the emergence of a new digital ecosystem where machines, AI agents, and human identities must coexist securely at unprecedented scale.
The implications are staggering. Organizations are grappling with identity sprawl where 60% manage over 21 identities per user, while AI-powered attacks have surged 3,000% for deepfake fraud and 700% for AI-generated phishing. Yet this same AI technology promises to revolutionize identity management through behavioral analytics, continuous authentication, and predictive threat detection. The industry has reached an inflection point where traditional perimeter-based security models are obsolete, and identity has become the new security perimeter.
From an entrepreneurial perspective, this transformation represents both the greatest opportunity and the most complex challenge the cybersecurity industry has faced. The global identity and access management market is projected to grow from $19.8 billion in 2024 to $61.74 billion by 2032, driven not just by digital transformation but by fundamental changes in how digital entities interact, authenticate, and establish trust.
The rise of non-human identities changes everything
The most striking revelation from Identiverse 2025 was the sheer scale of non-human identity proliferation. NHIs now outnumber human identities by as much as 100:1 in DevOps environments, with service accounts, API keys, workload identities, containers, microservices, and AI agents creating an identity explosion that traditional IAM systems simply weren't designed to handle.
Consider the scope: organizations average 82 machine identities per human employee, yet in cloud-native environments, this ratio reaches 40,000:1. These aren't just static service accounts—they're dynamic, ephemeral identities that spawn and dissolve based on workload demands, creating visibility gaps that attackers are already exploiting. The OWASP Non-Human Identities Top 10 framework, prominently featured at the conference, highlights risks that most security teams are only beginning to understand.
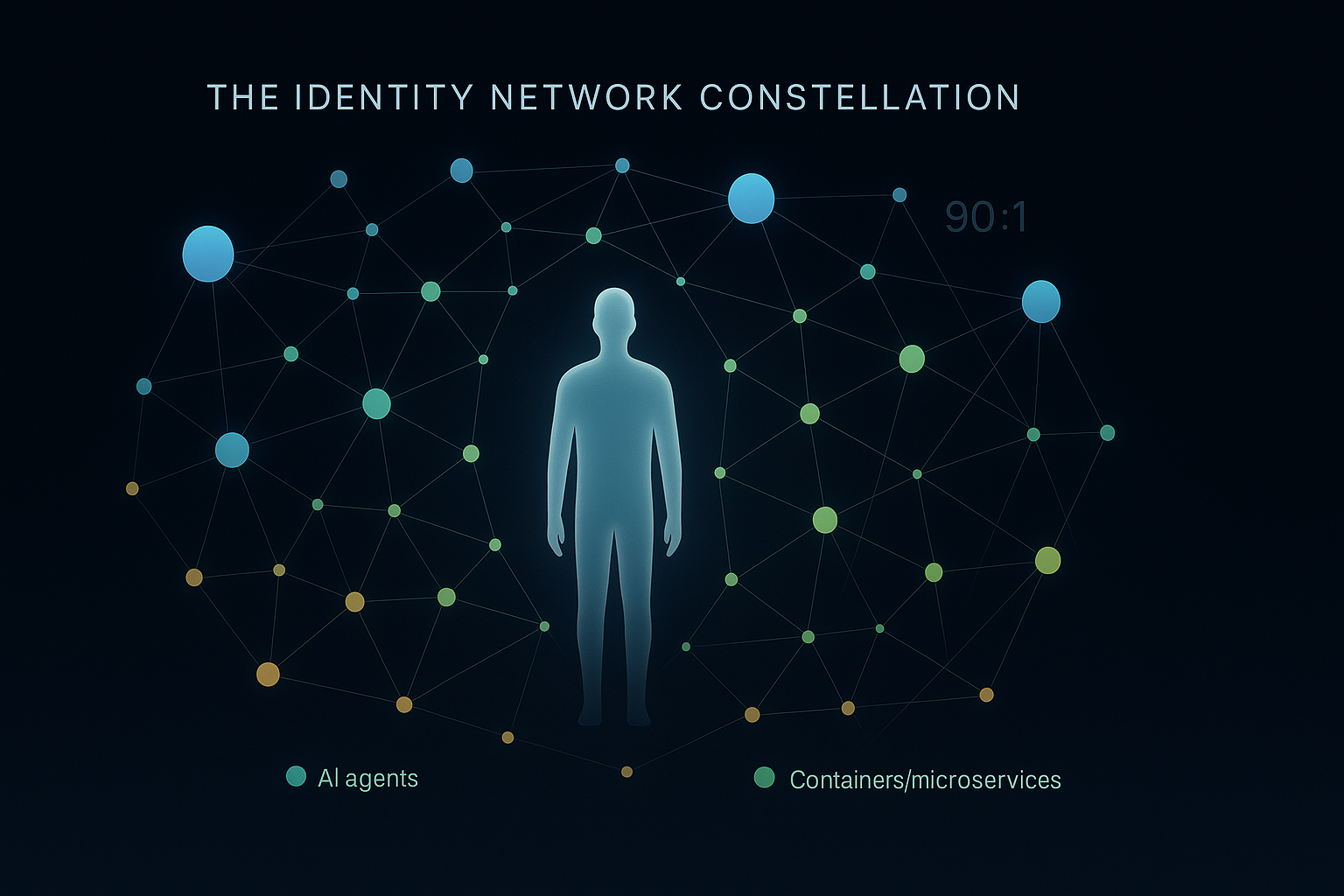
The challenge isn't merely about scale—it's about fundamental architectural assumptions. Traditional IAM systems were built around human identity patterns: predictable login times, consistent device usage, and relatively stable role assignments. Non-human identities operate on entirely different principles: they're programmatic, high-frequency, context-dependent, and often ephemeral. A container might exist for minutes, an API key might rotate hourly, and an AI agent might switch between multiple identities within a single transaction.
What makes this particularly complex is that only 5% of NHI permissions are actually used, yet over 50% are classified as high-risk. This represents a massive attack surface expansion where organizations are granting excessive privileges to identities they can barely track, let alone govern effectively. The traditional principle of least privilege becomes exponentially more complex when applied to thousands of machine identities operating at machine speed.
AI transforms identity management with dual-edged complexity
Artificial intelligence's impact on identity management embodies the classic double-edged sword—it's simultaneously the solution to our most pressing security challenges and the source of unprecedented new threats. At Identiverse 2025, sessions like "Who Am I When I'm Not Me? Identity in the Age of AI Agents" captured this paradox perfectly.
On the defensive side, AI is revolutionizing identity security through behavioral biometrics that analyze typing patterns, mouse movements, and interaction behaviors with remarkable precision. Machine learning algorithms can now detect anomalies in user behavior within milliseconds, enabling continuous authentication that adapts to risk in real-time. Organizations implementing AI-driven fraud detection report 74% improvement in accuracy while reducing false positives that traditionally frustrated users.
The power of AI-enhanced identity verification is evident in document authentication, where systems now utilize 35+ proprietary AI models trained on real-world datasets to detect forgeries, morphing attacks, and synthetic documents with unprecedented accuracy. Liveness detection for biometric authentication now exceeds 99% accuracy for enterprise-grade solutions, making sophisticated spoofing attacks significantly more difficult.
However, the offensive capabilities that AI provides to attackers are equally impressive and concerning. The 3,000% increase in deepfake-driven identity fraud represents more than statistical growth—it signals a fundamental shift in the threat landscape. AI-generated synthetic identities, voice cloning for social engineering, and deepfake video calls targeting executives are no longer theoretical risks but operational realities that security teams face daily.
Perhaps most concerning is the emergence of agentic AI systems that can autonomously switch between human and non-human identities, making access decisions without human oversight while potentially being manipulated through prompt injection attacks. These AI agents require new authentication paradigms that traditional OAuth and SAML systems simply cannot provide.
Passwordless authentication reaches enterprise maturity
The passwordless revolution has moved beyond proof-of-concept to enterprise-scale deployment, with 50% of US enterprises now implementing some form of passwordless authentication. Gartner's prediction that 75% of workforce authentication transactions will be passwordless by 2027 is already materializing faster than anticipated, driven by improved user experience and demonstrable security benefits.
The technical foundation is solid: passkeys are enabled on over 90% of iOS and Android devices, and WebAuthn support is universal across major browsers. Organizations like Accenture report 60% reduction in phishing attacks after implementing Windows Hello for Business across all devices, while Discord achieved 100% phishing-resistant authentication for their workforce through mandatory security keys.
From an implementation perspective, the convergence of identity wallets and passkeys represents the most significant authentication advancement since multi-factor authentication. The ability to store credentials securely on devices while maintaining cross-platform synchronization addresses the historical trade-offs between security and convenience. Christine Owen from 1Kosmos noted this convergence as driving "the next wave of passwordless authentication solutions."
The market dynamics support this trend: the global passwordless authentication market grew from $18.82 billion in 2024 to $21.58 billion in 2025, with projections reaching $86.35 billion by 2033. These aren't just aspirational forecasts—they reflect real enterprise spending on technologies that deliver measurable ROI through reduced support costs and improved security posture.
However, implementation challenges remain significant. 67% of organizations face compatibility issues with existing infrastructure, and the initial investment averaging $1 million for large enterprises requires careful ROI planning. The key to successful passwordless adoption lies in phased implementations that start with high-risk user groups and critical applications while maintaining robust fallback mechanisms.
Fraud prevention evolves through intelligent automation
The evolution of fraud prevention in identity management reflects the broader shift toward intelligent, automated security systems that can operate at the speed and scale of modern digital interactions. Traditional rule-based fraud detection systems are being replaced by AI-powered behavioral analytics that continuously learn and adapt to emerging threats.
The statistics are compelling: machine learning algorithms now reduce credit card fraud detection time to milliseconds while achieving 74% improvement in accuracy. The US Treasury's recovery of $4 billion through ML-enhanced fraud prevention demonstrates the real-world impact of these technologies at scale.
What's particularly interesting is the shift toward multi-modal fraud detection that combines traditional identity verification with behavioral analysis, device intelligence, and contextual risk assessment. Modern systems analyze typing patterns, mouse movements, navigation behavior, and even subtle biometric characteristics to create unique identity profiles that are extremely difficult to replicate or steal.
The emergence of synthetic identity detection represents a crucial advancement as criminals increasingly use AI to create entirely fabricated identities rather than stealing existing ones. These sophisticated attacks require equally sophisticated defenses that can analyze document authenticity, cross-reference identity attributes across multiple databases, and identify patterns that indicate artificial identity construction.
However, the arms race continues to escalate. Morphing attacks using AI face-swap technology now pose significant challenges for passport control and high-security applications. Organizations must balance increasingly sophisticated fraud prevention capabilities with user privacy concerns and regulatory compliance requirements across multiple jurisdictions.
Digital identity wallets promise enhanced privacy and control
The digital identity wallet revolution represents perhaps the most user-empowering development in identity management, shifting control from centralized authorities to individuals while maintaining security and privacy. The EU Digital Identity Wallet framework implementation deadline of 2025 is driving global adoption, with 60% of the global population anticipated to use digital wallets by 2026.
The architecture is compelling: self-sovereign identity (SSI) principles combined with blockchain-based credential verification create tamper-resistant records while enabling selective disclosure. Users can prove specific attributes—age, citizenship, professional credentials—without revealing unnecessary personal information. This addresses the fundamental privacy challenge of traditional identity systems that require over-collection of data to function effectively.
The technical implementation involves verifiable credentials (VCs) following W3C standards and decentralized identifiers (DIDs) that eliminate dependencies on central authorities. When combined with zero-knowledge proofs, users can demonstrate identity attributes without revealing the underlying data—proving they're over 21 without disclosing their actual birthdate, for instance.
Real-world adoption is accelerating: 87% of pilot participants express strong interest in comprehensive digital ID wallets, particularly when they provide seamless integration with existing services while enhancing privacy. The TSA's acceptance of digital driver's licenses and state implementations across California, Louisiana, and Arizona demonstrate practical applications that users can experience today.
The enterprise implications are significant. Organizations can implement privacy-by-design identity verification that meets stringent regulatory requirements while reducing data liability. By relying on verifiable credentials rather than collecting and storing personal information, companies can minimize their exposure to data breaches while improving user trust.
Enterprise challenges demand strategic identity architecture
The reality for enterprise organizations is that identity management has evolved from a compliance requirement to a strategic business enabler that directly impacts operational efficiency, security posture, and competitive advantage. The challenge lies in managing this complexity while maintaining security and user experience.
Current enterprise environments are characterized by 60% of organizations managing over 21 identities per user, creating sprawl that traditional governance frameworks cannot effectively manage. When combined with hybrid work environments where 97% of employees use personal devices for work and multi-cloud architectures that span dozens of platforms, the identity governance challenge becomes exponential.
The cost implications are substantial. Modern identity verification systems require initial investments averaging $1 million for large enterprises, with ongoing operational costs including per-transaction processing fees, infrastructure maintenance, and compliance monitoring. However, organizations that implement comprehensive identity governance report significant ROI through reduced security incidents, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced regulatory compliance.
Zero-trust architecture adoption represents the most significant strategic shift, with Gartner predicting 60% of enterprises will embrace zero-trust as a security starting point by 2025. This isn't merely a technology upgrade—it's a fundamental reimagining of security architecture where identity becomes the primary control plane for access decisions.
The implementation challenges are significant: 51% of organizations struggle with outdated technology and technical debt, while 40% lack adequate resources for comprehensive identity programs. Success requires executive sponsorship, cross-functional collaboration, and a phased approach that balances immediate security improvements with long-term architectural vision.
Strategic implications for the digital trust economy
The transformation of identity management represents the emergence of a digital trust economy where identity verification, authentication, and authorization become foundational services that enable everything from AI agent interactions to cross-border commerce. Organizations that successfully navigate this transformation will establish themselves as leaders in digital trust, while those that lag risk significant security exposure and competitive disadvantage.
From a strategic perspective, identity is becoming the new networking layer of the digital economy. Just as TCP/IP enabled the internet's explosive growth by providing reliable packet routing, modern identity systems enable secure, scalable digital interactions between humans, machines, and AI agents. The organizations that master this identity layer will have significant advantages in deploying AI, enabling digital transformation, and creating new business models.
The investment implications are substantial. Venture capital investment in identity startups continues to grow, with private equity showing renewed interest in identity security companies. CyberArk's $1.54 billion acquisition of Venafi and Permira's $1.3 billion investment in BioCatch demonstrate the market's recognition of identity as a critical infrastructure investment.
Regulatory evolution will continue to shape the industry, with AI governance requirements, expanded privacy regulations, and post-quantum cryptography mandates creating both compliance challenges and market opportunities. Organizations that proactively address these requirements will avoid costly retrofits while positioning themselves as trusted partners for regulated industries.
The path forward: building identity-centric security
The future of cybersecurity is identity-centric, and the organizations that recognize this shift earliest will have the greatest advantages. This isn't about implementing another security tool—it's about fundamentally rethinking security architecture around identity as the primary control plane.
Immediate priorities should focus on zero-trust implementation, AI defense integration, passwordless transition, and comprehensive machine identity management. These aren't separate initiatives but interconnected components of a modern identity security fabric that can scale with organizational growth and technological change.
Medium-term strategy requires development of integrated identity platforms that span IAM, PAM, and governance while preparing for decentralized identity systems and quantum-safe cryptography. This architectural foundation will enable organizations to adapt quickly to emerging technologies and regulatory requirements.
Long-term positioning involves preparing for sovereign identity ecosystems, predictive identity security, ambient authentication, and cross-border interoperability. These capabilities will define competitive advantage in the digital economy of the 2030s.
The identity industry's evolution from access control to comprehensive digital trust platforms represents one of the most significant technology shifts of our era. The companies that master identity management will control the foundational layer of digital trust that enables everything from AI deployment to global commerce. The question isn't whether to invest in identity security—it's whether you'll lead this transformation or be forced to follow.
The age of identity-centric security has arrived. The organizations that embrace this shift will thrive in an AI-powered, machine-abundant digital future. Those that cling to perimeter-based security models will find themselves increasingly vulnerable in a world where the perimeter has dissolved and identity is everything.

